Guatemala
Guatemalan coffee has been a staple of our offerings since our very early days, and it is one of our most treasured origins.
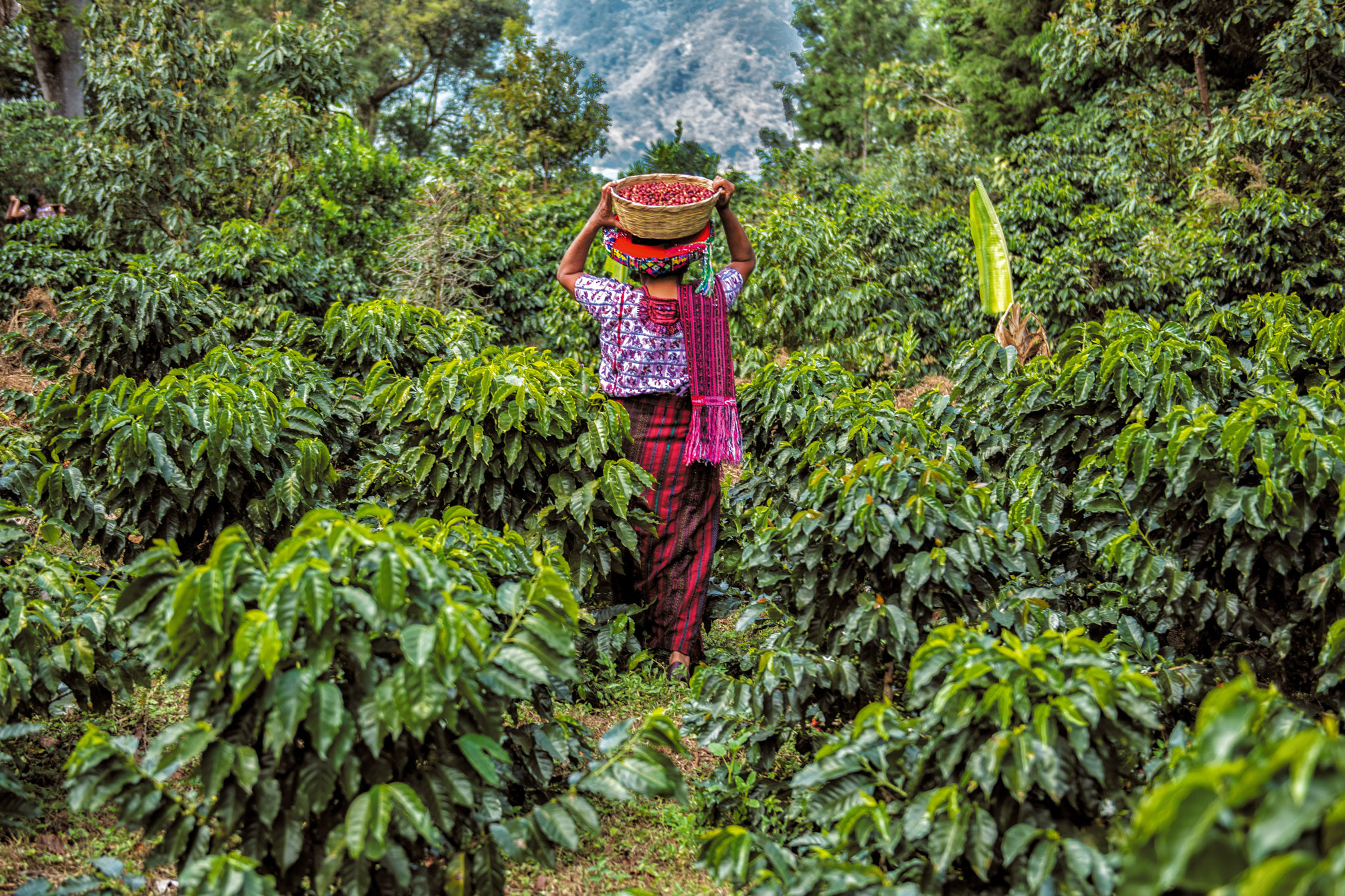
We love the distinctly unique and delicious flavour profiles that can be found in Guatemala, which are a result of the incredible range of microclimates that exist across each of the country’s coffee-growing regions. We have been lucky enough to work with many of the same estates in Guatemala since 2008, and every year we’ve been impressed with the quality and consistency of the coffee produced there.
Guatemala is the eighth biggest exporter of coffee in the world. Coffee accounts for 40% of the national agricultural export revenue, and it is estimated that there are over 125,000 producers of coffee across the country. Many of these are smallholders, who are either working independently or formally affiliated with a cooperative or growers association.
Nearly all the coffee produced in Guatemala is Arabica and is processed using the washed method, thanks to the abundant water supply available. Large-scale family-run estates, which have a long history of coffee farming and technical expertise, have had the scale and resources to refine and evolve their farming practices over time. Many of these farmers have their own wet mills and drying facilities, enabling them a great deal of control over the way the coffee is processed. Over time, small-scale producers have inherited some of this knowledge and applied it in their own farms, creating a well-resourced and diverse coffee community.
History of Coffee in Guatemala
Coffee was introduced to Guatemala by Jesuit priests as a decorative garden plant in the 1700s. Though it was consumed by some of the country’s foreign population, it was not planted commercially until the 1850s, when the government began offering land as an incentive to prospective growers. The coffee sector steadily grew in the following decades and began to receive international acclaim – gaining recognition as the “the finest coffee in the world” at the 1888 World Fair in Paris, and the 1915 San Francisco Exposition – and culminating with the founding of the Guatemalan National Coffee Association (Anacafé).
Established in 1960, Anacafé provides producers with technical assistance and education, with the goal of helping Guatemalan growers improve their quality of output and yield. The organisation invests heavily in research, advocates for infrastructure improvements within the country, and provides extension services to producers, such as soil, water and leaf analysis (to help farmers ensure adequate nutrition and fertilisation) and sensory analysis (providing feedback on samples submitted by producers).
Anacafé also helps market Guatemalan coffees nationally and internationally and has a department dedicated to promoting social development programs within the coffee sector, with a focus on food security, nutrition and health. By providing farmers with an incredibly strong system of support and promoting the highest standards in every aspect of coffee production, the association has ensured both small and large producers can achieve a viable future in coffee production. It is one of the most open, transparent and well-run coffee organisations we’ve come across, and the best cuppers in the country were trained at its lab in Guatemala City.
Our Supply Partners
In Guatemala, we have direct sourcing relationships with several producers, many of whom we have been lucky to work with for over a decade. For all of them, coffee is more than just a cash crop. It is a family tradition and a great source of pride; something they are incredibly passionate and knowledgeable about and deeply invested in. Our supply partners include Ricardo Zelaya (Santa Clara, Hacienda Carmona) and Rony and Lucia Asensio (La Soledad) – who are all part of Zelcafe; and Luis Valdés of Santa Isabel. All of these individuals produce exceptional coffee every year, and we feel very privileged to represent their coffees in Australia.
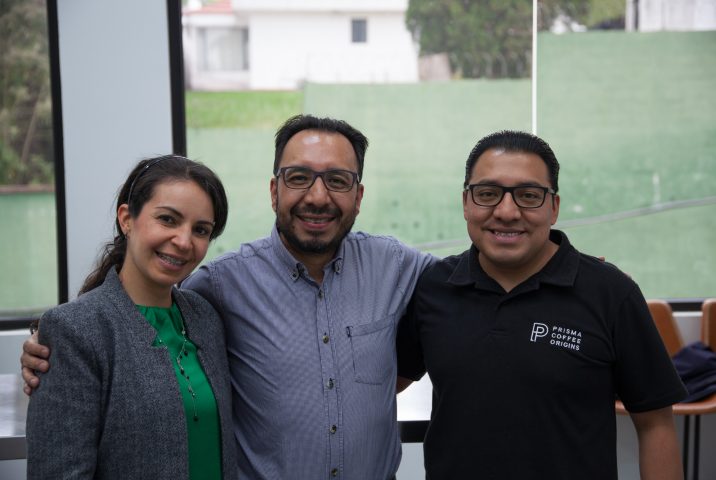
In addition, we are fortunate to work with Eduardo Ambrocio of Prisma Coffee. Eduardo worked at Anacafé for two decades (heading the Quality Control department for many of those years) and was pivotal in setting up the Cup of Excellence in Guatemala in 2001. We first met him in 2010 during a Cup of Excellence competition, and fell in love with the infectious enthusiasm he described his favourite coffees, sharing stories of the people behind them with evident respect and admiration for their hard work and expertise. Eduardo went on to establish Prisma with his wife Lucia and brother Edwin in 2013. Together, the trio source some of the very best coffees Guatemala has to offer, and support small producers from more remote areas of the country to gain access to quality-focused buyers who are willing to pay a premium for quality. Through Prisma, we have been able to establish relationships with some of these smaller-scale producers, including Darwin Fabián of El Calagual and Nery Pablo of Guacamaya.
Key Coffee-Growing Regions
Coffee is grown in 20 of Guatemala’s 22 departments. High elevations (1,300m-2,000m above sea level), combined with rich volcanic soil (from the 35+ volcanoes across the Guatemalan highlands) and more than 300 microclimates means that Guatemala is able to produce exceptional coffees with a wide range of flavours, which can vary greatly depending on where they are grown.
Some 98% of coffee in Guatemala is shade-grown. These trees prevent erosion and provide important soil nourishment, infusing the soil with nitrogen and other nutrients via the organic matter created by their decaying leaves. In addition, their added foliage moderate the intensity and quality of sunlight, helping to regulate the coffee trees’ respiration and photosynthesis, and protecting the coffee roots and leaves from sun damage. Shade cover also allows the coffee beans to mature more slowly, enhancing the resulting sweetness, acidity and complexity in the cup.
Guatemala coffee plantations cover more than 270,000 hectares, with an estimated 38 million shade trees and coffee plants making up 6.4% of the nation’s forest cover. These coffee ‘forests’ are typically located on steep mountain ranges, in important water recharge areas, and help to protect the country’s ecological health by aiding in the preservation of local biodiversity, protecting watersheds and helping prevent erosion.
There are eight distinct Guatemalan coffee-growing regions that have been defined by ANACAFE based on cup profile, climate, soil and altitude: Antigua, Huehuetenango, San Marcos, Atitlán, Acatenango, Cobán, Fraijanes and New Oriente. We buy coffee from all over Guatemala, but the regions we work in the most are as follows:
ANTIGUA
The Antigua valley is bounded by three volcanoes – Hunahpú (also called Agua in Spanish), Chi Q’aq’ (also called Fuego) and Acatenango. Of the three, Chi Q’aq’ is the only one still active. On many visits, we have been in town at times the volcano has erupted, adding some chaos to the harvest (in the short term, the ash can stick to the leaves of coffee trees nearby and prevent the trees from photosynthesising), but ultimately providing mineral-rich ash for Antigua’s soil. This volcanic matter helps the soil retain its moisture, offsetting the region’s lower rainfall.
Coffee from Antigua is perhaps Guatemala’s best-known and most celebrated and, as such, typically attracts higher prices than coffee from other regions. They tend to be heavier bodied, with notes of dark chocolate, brown sugar and red apple. In 2000, Antigua received a Denomination of Origin to recognise the region as distinct, and to prevent other coffees from being marketed as Antiguan.
The region surrounding Antigua Guatemala is the traditional land of the Kaqchikel people, who were once one of Guatemala’s largest Mayan kingdoms. Their ancient capital, Iximché, is located some 50km from the Antigua valley, and was considered one of the country’s most important cities before the Spanish invasion of Guatemala. The Kaqchikel are remarkable historians, and their oral and written traditions (compiled in The Annals of the Kaqchikel) have been an important resource in preserving the cultural heritage of many of Guatemala’s indigenous communities.
Coffees from Antigua tend to be heavier bodied, with notes of dark chocolate, brown sugar and red apple. Some of our favourite coffees come from this region, including Santa Clara, La Soledad and Hacienda Carmona.
ACATENANGO
Located west of Antigua, beyond the Acatenango and Fuego volcanoes, is the Acatenango valley. Like Antigua, this distinct and special growing region has also been recognised with a Designation of Origin. Due to their proximity, the regions’ economies are linked and many of Acatenango’s people work in or near Antigua, in addition to farming coffee and other products closer to home.
The region benefits from frequent eruptions from the nearby Fuego Volcano, which keep the coarse, sandy soils full of minerals. Coffee here is grown under dense shade of Gravilea, Inga, and Guachipilín trees, at elevations of up to 2,000 meters above sea level, creating an incredibly biodiverse forest environment.
Due to its location, Acatenango also experiences temperate gusts from the Pacific Ocean and a marked dry season. This allows for coffee to be fully sun-dried without much need of mechanical aids, like Erick and German de la Roca aim to at their farm, La Esperanza.
HUEHUETENANGO
Huehuetenango (or HueHue as it is often called) is a stunning region located in the west of Guatemala near the border of Mexico. HueHue is known for being home to the Cuchumatanes mountain range, the highest non-volcanic mountain range in Central America, and for its vast ethnic diversity, which includes the Mam, Q’anjob’al, Chun and Jakalteko people. Before the Spanish invasion, the region was known as Xinabajul, which translates to “between ravines” in the local Mam language and is a reference to the numerous cliffs and steep hills found throughout the department. Pre-colonisation, the region’s largest city was Zaculeu (found in the outskirts of modern Huehue City), which translates to “white earth,” and whose ruins can still be visited today.
The department is vast, and includes a number of types of terrain that are suited to different forms of agriculture, depending on the elevation. Corn is the main staple of the lower regions, which transitions into coffee the further up one goes, with local pine farmed throughout the entire department. Huehue’s coffee-growing regions produce some of the most complex and celebrated lots in the country, and the region frequently appear in the top ten of the Cup of Excellence competition. This is in part due to the incredibly high elevations that coffee can grow (up to 2,000m above sea level), thanks to the dry, hot winds that blow into the mountains from Mexico’s Tehuantepec plain and protect the region from frost. These high elevations combined with a relatively predictable climate make for exceptional quality coffee. The highest elevations in Huehue, above 2,100m above sea level, are quite dry and rocky, so most farmers dedicate themselves to growing potatoes and herding sheep, goats and llamas.
Coffees from HueHue tend to be incredibly floral and complex, and very fruit-driven. Some of our favourite coffees come from the region, including La Providencia, Calahute and La Maravilla.
COBÁN & BAJA VERAPAZ
The municipality of Alta Verapaz and capital city Cobán are known for their lush rainforest and cool and very wet climate – with an annual precipitation of 3,500m, and regular rainfall throughout the year. This results in a very slow maturation time for the coffees (which can help produce very sweet and complex flavour profiles), with staggered flowering and ripening requiring producers to make as many as ten passes throughout the season to ensure only the ripest cherries are selected. The wet climate can provide a challenge for coffee drying, and the region’s remoteness also provides some barriers for producers. With great care, however, some truly exceptional coffees are produced in this region, including crowd-favourite Santa Isabel.
Historically, the region is home to the Q’eqchi’ people, whose name for Alta Verapaz is Tucurután, (also spelled Tezulutlán), translating to “Land of War.” The Q’eqchi’ were known as fierce warriors who put up great resistance during the Spanish invasion of Guatemala, leading to considerable bloodshed, persecution and forced migration. While the centuries following the conquista have been difficult for the Q’eqchi’ – who lost right to all communal lands and continue to experience political conflict today – many of the community leaders play a key role in the region’s efforts towards environmental conservation. They have been able to pass down their knowledge on preserving the local biodiversity, as well as the propagation and cultivation of many native plant species in the municipality.
SANTA ROSA
Though the Santa Rosa department is technically not one of ANACAFE’s official coffee-growing origins, in recent years it has become one of the country’s most recognised regions. Farms in Santa Rosa are spread out across the expanse of the department – meaning climatic conditions vary drastically from one estate to another, resulting in a multitude of unique cup profiles.
The region is known for producing much of the country’s commercial-grade coffee, but the range of micro-climates and rich, volcanic soils found in Santa Rosa offer great potential for specialty-grade coffee production. This is evident from the 2022 Cup of Excellence results, when 5 coffees from Santa Rosa were awarded for the first time in the competition’s history.
The department’s north is a valley surrounded by mountains, creating a corridor for dry winds from the Atlantic Ocean to travel south all the way to the Pacific. Because of this, conditions in the north tend to be drier and experience earlier harvests (like in La Bugambilia and El Calagual), while the south is more humid and experiences longer rainier seasons.
Santa Rosa is the traditional home of the Xinka people, some of Guatemala’s earliest inhabitants. Having arrived from the Andes mountains via the Pacific Ocean, the Xinka are one of the country’s only indigenous communities that does not share cultural or linguistic similarities with the Maya, Guatemala’s largest indigenous group. While less than two-percent of the modern-day population identify as Xinka, they have become one of the loudest voices in the fight for Guatemala’s environmental preservation. In recent years, the Xinka have stood up to multinational mining companies that buy up land and destroy established farms in search for silver. The community has banded together and fought to be recognised as the region’s traditional owners, who want their land to be used for more environmentally and socially sustainable projects.
FRAIJANES
ABOUT FRAIJANES
Located a mere 40-minute drive from Guatemala City is Fraijanes, one of Guatemala’s oldest coffee-growing regions. Its proximity to the country’s capital was pivotal in its early days, as it helped transform the region into one of the country’s most productive. As the city grew and its population swelled, urban expansion pushed many coffee estates out of Fraijanes, with many of the local farm workers choosing to move away from their rural communities to find work in the city.
The region is known for its volcanic pumice soil, very high altitudes and plentiful rain during the wet season. Fraijanes is bordered to the west by Pacaya, one of Guatemala’s three active volcanoes. Similar to Chi Q’aq’ (also known as Fuego) Volcano in Antigua, Pacaya releases light deposits of ash every so often, boosting the mineral content of the region’s soils.
Although early mornings in Fraijanes are cloudy and foggy, days are mostly sunny. The dry season is particularly warm, which creates the perfect conditions for drying coffee without much need of mechanical aid. In recent years, these climatic conditions have been harnessed by farmers who focus on specially prepared lots, like those produced at Agua Tibia.